Introduction
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) presents significant opportunities and challenges across various sectors, including content creation, media, and technology. As AI continues to generate content, its ethical implications have become increasingly important. Ethical AI emphasizes integrating fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI applications. A key component of this ethical framework is the implementation of content watermarking, a method designed to identify and verify AI-generated materials.
Watermarking serves to enhance transparency by allowing users to distinguish between AI-generated content and human-produced material. This is critical in mitigating misinformation, as unmarked AI-generated content can mislead audiences and exacerbate issues surrounding trust in media. Additionally, watermarking embeds accountability in content creation, empowering developers and content creators to take responsibility for the outputs generated by AI technologies.
As the importance of watermarking becomes clearer, industry stakeholders must familiarize themselves with effective implementation techniques, comply with emerging regulations, and understand the ethical landscape surrounding AI. This guide aims to provide AI developers and content creators with a comprehensive overview of ethical AI frameworks, focusing on the need for transparency through content watermarking. It will address practical insights, technical methods, compliance issues, and the importance of media literacy in navigating the evolving AI landscape.
Understanding Ethical AI and the Necessity for Watermarking
Ethical AI refers to principles that guide the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies. These principles emphasize values such as fairness, accountability, and transparency, which are vital for building trust between AI developers and users. The need for transparency in AI-generated content has increased, especially with the proliferation of misinformation and the potential for AI systems to manipulate public opinion.
Watermarking plays a crucial role in ensuring that audiences can identify AI-generated content, thereby reducing misinformation's spread. According to Google's SynthID, unmarked AI content can mislead users; hence, robust identification mechanisms are essential. Watermarking not only helps to deter misleading practices but also fosters consumer trust, allowing users to engage with AI content more responsibly.
The increasing demand for transparency is largely due to the growing integration of AI in everyday applications—from news articles and social media posts to videos and audio recordings. In this context, ethical AI frameworks must prioritize watermarking as a fundamental element of content creation. The European Union's AI Act emphasizes the ethical responsibilities that AI developers must integrate into their frameworks, highlighting the need to mark AI-generated content to maintain user awareness and trust.
This infographic outlines the ethical responsibilities of AI developers alongside key statistics related to misinformation in AI usage. (Source: Infotrends)
Decoding Watermarking Techniques for Various Media Types
Watermarking techniques have evolved significantly and can be categorized based on the type of media: text, images, audio, and video. Each media type presents unique challenges and opportunities for effective watermarking.
Text Watermarking
Text watermarking employs statistical methods to create patterns or signals that are discernible only through specialized detection algorithms. Statistical watermarking utilizes linguistic patterns, which enable the embedding of imperceptible markers within the text. This process is vital, as it addresses the challenges associated with embedding visible identifiers.
Image Watermarking
For images, watermarking techniques can be broadly classified into deep learning-based approaches and traditional methods. Google’s SynthID demonstrates how deep learning can embed watermarks in the latent space of images, allowing for robust detection even after transformations such as cropping. Traditional methods, such as Least Significant Bit (LSB) insertion and frequency-domain techniques (e.g., Discrete Cosine Transform), also play significant roles, although they may face challenges with image alterations.
Audio Watermarking
Digital signal processing methods are utilized for audio watermarking, where minor alterations are made to sound waveforms—imperceptible to human ears—while preserving audio quality. Nonetheless, this area faces challenges regarding quality retention and resistance to modifications.
Video Watermarking
Video watermarking integrates techniques from both image and audio watermarking, embedding markers across multiple frames. However, the computational demands and potential for aesthetic degradation present challenges to the effectiveness of these techniques.
Despite these advances, ongoing research aims to improve robustness and imperceptibility across all media types. Recent advancements in statistical watermarking, particularly for text, present a promising avenue for enhancing regulatory compliance and ethical AI use while mitigating the risks associated with misinformation.

This diagram presents various techniques for watermarking across different media, providing insights into how watermarking can effectively safeguard content. (Source: ResearchGate)
Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Frameworks for Watermarking
Understanding the legal landscape governing AI-generated content is essential for developers and content creators. In the United States and Europe, regulatory initiatives are emerging to establish standards for watermarking and content authenticity.
EU AI Act
The EU AI Act, provisionally agreed upon in December 2023, represents a significant step in regulating AI technologies. Among its provisions, the act mandates that AI-generated or altered content must be clearly labeled, and that AI systems should embed watermarks in a machine-readable format. This requirement aims to enhance user awareness and trust. However, the act also acknowledges the current technical limitations of watermarking techniques, emphasizing a need for ongoing research and development.
US Regulations
In contrast, the regulatory environment in the United States is evolving. The Biden Administration's Executive Order on AI, issued in October 2023, instructs the Department of Commerce to develop standards concerning watermarking and content provenance. Additionally, California's AI Transparency Act, passed in September 2024, mandates organizations to provide detection tools and clear disclosures regarding AI-generated content.
These regulations underscore the importance of compliance for content creators as they navigate both federal and state-level laws. Additionally, the effectiveness of compliance mechanisms will hinge on adopting and implementing robust watermarking practices, demonstrating the necessity for developers to stay informed about evolving legal requirements.

This chart compares the regulatory frameworks of the EU and US regarding AI-generated content and watermarking requirements, highlighting key differences. (Source: GABI Journal)
The Dual Role of Human Oversight in AI-Generated Content
Human oversight remains an indispensable element in the development and deployment of AI-generated content. A balanced approach that integrates human scrutiny can greatly enhance ethical practices.
Mitigating AI Risks
Human oversight serves as a check against the potential pitfalls of relying solely on automated systems. By ensuring that trained professionals assess AI outputs, organizations can identify and rectify issues that algorithms may overlook. For instance, developers can monitor for biases and inaccuracies that may arise within AI-generated content, contributing to more responsible usage.
Case Studies of Effective Oversight
Several case studies illustrate the successful integration of human oversight in AI processes. For example, organizations that employ human reviewers to assess AI-generated news articles have reported a reduction in misleading or harmful content. Experts emphasize that human involvement adds accountability, enhancing the reliability of AI systems.
Potential Oversight Failures
Despite these benefits, areas where human oversight may fail must be acknowledged. In situations requiring rapid decisions, there is a risk that oversight may be compromised, underscoring the need for ongoing training and clear protocols to guide human reviewers.
In summary, optimizing human oversight in AI-generated content not only aids in mitigating risks but also reinforces ethical standards within the industry. By embracing this duality, organizations can position themselves to create more transparent and trustworthy AI outputs.

This flowchart visually represents the interaction between human oversight and AI processes, emphasizing the importance of human roles in AI workflows. (Source: ResearchGate)
Balancing Innovation and Responsibility in AI Usage
As the application of AI technology expands, the need to balance innovation with ethical responsibility becomes paramount. This section explores how organizations can foster innovation while embedding ethical practices.
Fostering Innovation
AI's transformative potential offers unprecedented opportunities for innovation across various industries. Ethical frameworks must be integrated into the design and deployment of AI systems to ensure that these innovations do not compromise ethical standards. Organizations can encourage teams to innovate responsibly by establishing clear ethical guidelines that provide a framework for assessing technological advancements.
Cultural Impact of AI
The influence of AI-generated content extends into cultural aspects, shaping public perceptions and societal norms. It is crucial for organizations to consider the cultural ramifications of AI innovations, as they can inadvertently reinforce biases or stereotypes. By prioritizing ethical considerations, developers can create content that promotes inclusivity and respect.
Successful Innovations with Ethical Considerations
Organizations successfully integrating ethical considerations into their AI innovations serve as powerful examples. For instance, companies that pursue fairness in content generation through diverse training datasets showcase a commitment to responsible AI use. Moreover, initiatives focused on transparency, such as sharing information about AI decision-making processes with users, enhance public trust in AI technologies.
In conclusion, the need to balance innovation with ethical responsibility is critical. As AI technologies continue to evolve, developers and content creators must strive to align their innovations with ethical principles to ensure they contribute positively to society.

This thematic illustration effectively juxtaposes innovation with accountability in AI use, capturing the balance developers must maintain. (Source: SwissCognitive)
Empowering Communities with Media Literacy and Public Education
Media literacy and public education are essential in fostering a better understanding of AI-generated content. This section discusses the importance of empowering users and highlights various initiatives aimed at enhancing media literacy.
Role of Media Literacy
Media literacy education equips individuals with the critical thinking skills needed to navigate the complexities of AI-generated content. By fostering awareness of potential misinformation, users become more adept at distinguishing between authentic and manipulated content. A UC Berkeley study underscores the significant role critical thinking plays in enabling individuals to identify AI-generated materials.
Educational Initiatives
Recent initiatives emphasize the value of public education on AI technologies. The Biden Administration’s Executive Order on AI highlights the necessity for public awareness campaigns educating consumers about AI-generated content. Concurrently, California's proposed AI Literacy Bill aims to integrate AI education into school curricula, ensuring that students develop a nuanced understanding of AI technologies.
Enhancing Watermarking Effectiveness
Increasing media literacy directly impacts the effectiveness of watermarking efforts. As users become more educated about AI and its implications, they will better understand the significance of detecting AI-generated content. Furthermore, informed users can actively participate in discussions surrounding regulatory approaches and ethical considerations.
In summary, enhancing media literacy and public education is critical in promoting responsible consumption of AI-generated content. By empowering individuals with the tools to critically evaluate media, organizations can create an informed community capable of engaging with technology responsibly.
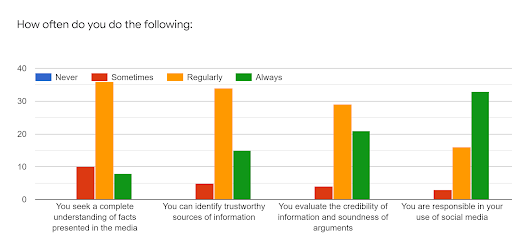
This graph demonstrates trends in media literacy education, showcasing its role in fostering understanding of digital content and AI-generated materials. (Source: CAPTA)
Conclusion
The landscape of ethical AI frameworks necessitates a balanced approach that emphasizes innovation alongside ethical responsibility. Implementing transparent content watermarking is central to enhancing user trust and accountability in AI-generated materials. By understanding the diverse watermarking techniques available, recognizing the regulatory landscape, and acknowledging the role of human oversight, developers and content creators can navigate the complexities of AI responsibly.
Moreover, empowering communities through media literacy and public education fosters informed engagement with AI technologies. As AI continues to shape society, maintaining a commitment to ethical principles will be crucial in ensuring that these advancements align with societal values and priorities. By collectively embracing these challenges, the technology sector can harness the power of AI to create a positive impact on the future.
Overall, the integration of ethical principles, effective watermarking, and stakeholder collaboration will ultimately enhance the authenticity and reliability of AI-generated content, paving the way for a more responsible digital landscape.

评论(0)
登录 参与讨论或 .